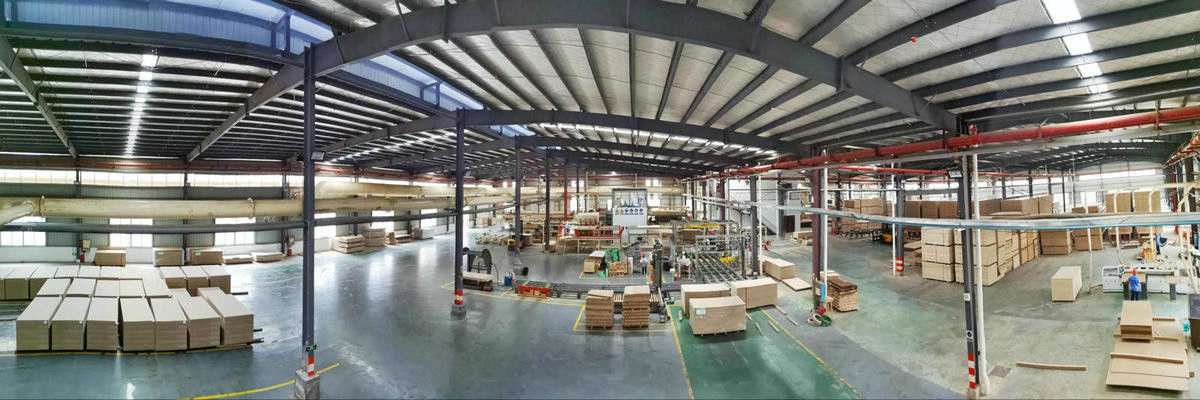
The Role of Automation in Modern OSB Production Lines and Its Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency
Automation has transformed the global engineered wood industry, and OSB (Oriented Strand Board) production is one of the sectors that has benefited the most from technological advancements. As demand increases across the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and other European regions, manufacturers face growing pressure to provide stable output, consistent product quality, and lower production costs. Automation has become the core solution for addressing these challenges. A modern automated OSB production line significantly improves efficiency, reduces labor requirements, enhances product consistency, and maximizes long-term profitability.
A fully automated OSB production line begins with raw material handling. Logs are fed into debarking systems equipped with hydraulic drives, intelligent sensors, and real-time feeding control. Automation ensures that logs are debarked uniformly and efficiently, preventing bark contamination in downstream processes. After debarking, logs are automatically conveyed to high-precision flakers. Modern flaking systems rely on PLCs and servo controls to deliver uniform strand geometry. Automation at this stage helps maintain predictable strength, moisture resistance, and mechanical performance in the finished OSB panels.
One of the most important automated stages involves strand drying. Automated dryers integrate temperature sensors, airflow regulators, humidity monitors, and fully programmable logic controllers. These systems automatically adjust drying parameters based on wood species, strand thickness, and moisture content. Automation ensures that strands reach the ideal moisture level for resin absorption. Over-drying or under-drying is minimized, which improves resin efficiency and prevents board failure during pressing.
Automated screening systems classify strands according to size. High-speed vibrating screens and optical sensors ensure that oversized or undersized strands are removed. This contributes to uniform panel density and consistent product performance. Automation eliminates the need for manual sorting and greatly improves classification accuracy.
Blending is one of the most critical steps in OSB manufacturing, and automation has enhanced it dramatically. Automated resin dosing systems adjust resin flow based on real-time feedback. These systems ensure optimal coating efficiency, reduce adhesive waste, and enhance bonding strength. Resin costs represent a significant portion of OSB production expenses, so precise dosing results in substantial savings. Automated blending also improves product consistency and reduces environmental emissions.
The forming stage has seen some of the most significant advancements in automation. Automated forming stations include multiple distribution heads, electronic alignment sensors, and computer-controlled strand orientation systems. These technologies arrange strands into multi-layer mats with exact weight, density, and orientation. Outer-layer strands are oriented parallel to the panel length, while core-layer strands are oriented perpendicular. Automated strand orientation enhances structural integrity, bending performance, and load-carrying capacity.
Pre-pressing and hot-pressing processes rely heavily on automation. Pre-press units use sensors and programmable settings to prepare mats for the final pressing stage. In the hot press, automated systems control temperature, pressure, press time, and board thickness. Continuous presses offer exceptional automation, allowing for dynamic adjustments and real-time optimization. This ensures reliable curing, uniform heating, and predictable mechanical performance.
After pressing, panels enter an automated finishing line. Cooling systems, trimming saws, edge milling machines, sanding systems, and inspection stations all operate under centralized control. Automated thickness gauges and optical scanners identify defects such as blisters, air pockets, density inconsistency, or damaged edges. Automated stacking and packaging systems prepare finished boards for shipment.
Automation not only enhances efficiency but also improves workplace safety. Manual labor is minimized, reducing the risk of accidents. Automated systems also improve environmental control. Dust filtration, cyclone separation, VOC absorption, and heat recovery systems are all automated to ensure compliance with U.S. EPA and European environmental regulations.
In the future, automation will continue to evolve with the integration of AI, machine learning, and predictive maintenance technologies. These enhancements will allow OSB manufacturers to anticipate maintenance needs, reduce downtime, and optimize production parameters even further. As global competition grows, manufacturers equipped with advanced automated OSB production lines will maintain a dominant position.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 
