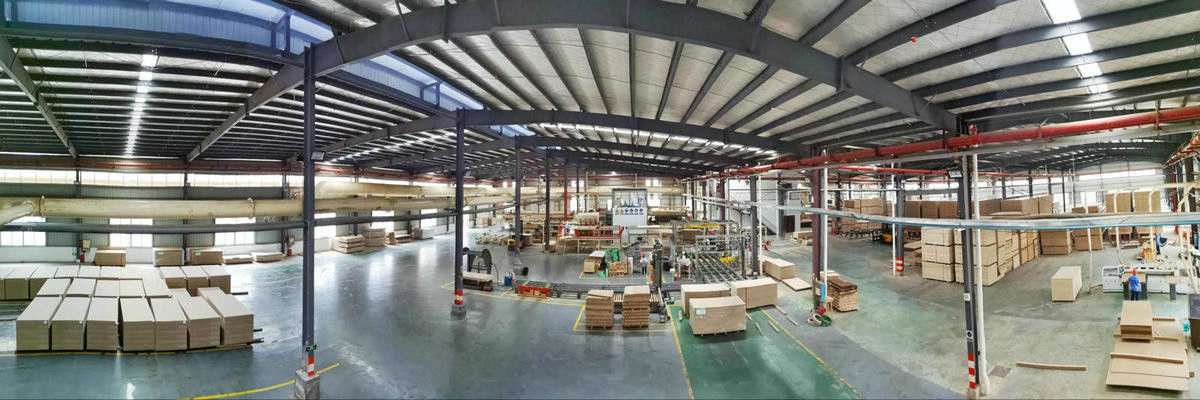
How a Modern OSB Production Line Improves Panel Strength, Efficiency, and Global Competitiveness
The OSB production industry is undergoing rapid development as global demand for construction materials, engineered wood products, and sustainable building solutions continues to increase. At the center of this expansion is the OSB production line, a fully integrated system designed to convert raw logs into high-performance structural panels suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. For companies supplying markets in North America and Europe, where product standards such as EN 300 and APA PS2 must be strictly met, a modern OSB production line has become essential for maintaining competitiveness. Advanced production technologies help improve panel strength, increase efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and ensure long-term operational stability.
An OSB production line performs a series of coordinated processes beginning with log preparation. Logs are debarked using drum debarkers or rotor debarkers to ensure that bark and impurities are effectively removed. This step is essential because bark contamination can reduce strand quality, introduce defects, and lower final panel durability. Once debarked, logs are cut into strands using high-precision flakers. Modern flaking systems include adjustable knife rings, servo-controlled feed mechanisms, and wear-resistant cutting blades that are capable of creating uniform strands even under demanding production conditions. Uniform strand geometry is one of the most important factors influencing the mechanical properties of finished panels, including bending stiffness, internal bond strength, and edge stability.
Strand drying is another crucial step in the OSB production line. Freshly cut strands contain significant moisture, and excessive moisture prevents proper bonding with resin. High-quality production lines utilize energy-efficient rotary drum dryers, triple-pass systems, or automated drying tunnels equipped with real-time moisture monitoring technology. These systems use temperature sensors, airflow regulators, and programmable logic controllers to maintain stable drying conditions and minimize energy waste. Drying strands to the correct moisture range ensures improved resin adhesion and consistent curing during pressing.
After drying, strands are screened and classified. Undersized or oversized strands are removed to maintain consistent board density and uniform mechanical performance. Blending is the stage at which strands are mixed with resin, wax, and additives. Resin dosing systems on modern OSB production lines provide precise chemical application rates, ensuring each strand receives the right amount of adhesive. Resin uniformity directly affects panel strength and water resistance. Structural OSB panels commonly use MDI resin due to its moisture resistance and high bonding strength. Automated blending equipment reduces waste, improves quality control, and increases production efficiency.
The forming process is one of the most sophisticated stages in an OSB production line. Strands are oriented into cross-directional layers to achieve desired mechanical performance. Forming machines employ oscillating distribution heads, belt conveyors, and electronic alignment systems to arrange strands accurately. The outer layers typically have strands aligned parallel to the panel’s length, while the core layer features strands oriented perpendicular. Precise control of this orientation results in superior bending performance, dimensional stability, and load-bearing capacity.
Once the mat is formed, it enters a pre-pressing section where air is extracted and the mat is compressed to a manageable thickness before hot pressing. Hot pressing is the core of the OSB manufacturing process. High-pressure, high-temperature presses consolidate the strand mat into a strong, durable panel. Continuous presses are increasingly used due to their consistent performance, higher output, and precise control over pressing parameters. Advanced hot-press systems monitor temperature distribution, pressure curves, heating plate performance, and panel thickness in real time, ensuring that each board meets international safety and performance standards.
After pressing, the panels enter the cooling and conditioning stage. Proper cooling prevents internal stresses and reduces warping. The panels then proceed to trimming saws, edge milling units, sanding machines, and calibration equipment. Sanding ensures accurate thickness tolerance, which is essential for structural applications and compliance with certification standards. Automated inspection systems scan panels for defects such as blisters, surface inconsistencies, density variations, or delamination. Ensuring consistent quality helps manufacturers reduce claim rates and maintain strong customer trust.
A modern OSB production line offers several distinct advantages. High automation levels reduce labor requirements and minimize human error. Energy-saving technologies lower operational costs and environmental impact. Dust-collection systems, gas exhaust filters, and VOC treatment solutions help manufacturers comply with European and North American environmental regulations. Digital control systems provide production traceability, real-time monitoring, and data analytics that support continuous improvement and predictive maintenance.
As markets shift toward sustainable building solutions, OSB has become a preferred material due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, renewable raw materials, and versatility. A modern OSB production line enables manufacturers to meet growing demand while maintaining competitive pricing and reliable quality. Companies that invest in advanced production technologies can establish strong market leadership, strengthen customer relationships, and increase long-term profitability.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 
